Machine Learning-Driven Optimization of TPMS Architected Materials Using Simulated Annealing
Akshansh Mishra·May 28, 2024
Summary
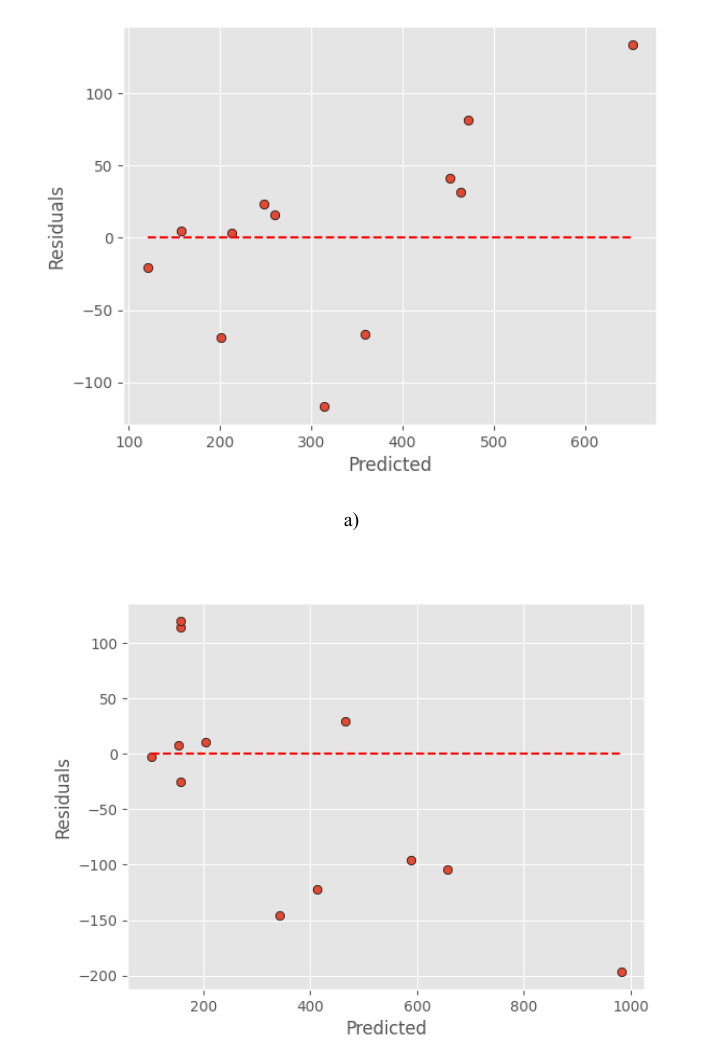
This paper investigates the use of machine learning, specifically Random Forest, Decision Tree, and XGBoost models, enhanced with Simulated Annealing (SA), to optimize tensile stress in Triply Periodic Minimal Surface (TPMS) structures. The SA-XGBoost model stands out with an R² value of 0.96, indicating its effectiveness in predicting stress. TPMS, known for their unique properties, have potential applications in various industries. The study combines computational methods and machine learning to improve the design process and efficiency of TPMS-architected materials, with implications for applications like biomedical, aeronautical, and automotive engineering. The research also highlights the potential for broader optimization of mechanical properties beyond tensile stress.
Advanced features