Democratizing Reward Design for Personal and Representative Value-Alignment
Carter Blair, Kate Larson, Edith Law·October 29, 2024
Summary
The paper introduces Interactive-Reflective Dialogue Alignment (IRDA), a method for personalizing AI reward design through iterative dialogue. It enables AI systems to learn individual value definitions, allowing for personalized AI behavior that reflects unique user preferences. Evaluated in two studies, IRDA accurately captures diverse value-aligned behaviors, offering a more representative and interpretable approach to AI alignment. The system uses a simple chat interface for users to explain desired behaviors and employs active learning techniques to gather feedback. IRDA creates a language-based reward model, leveraging large language models' in-context learning abilities. The system demonstrates the ability to capture diverse human values and ethical preferences more accurately than baseline systems.
Background
Overview of AI Alignment
Importance of aligning AI systems with human values
Challenges in designing AI rewards that reflect diverse human preferences
Introduction to IRDA
Purpose and motivation behind the development of IRDA
Unique approach of IRDA in personalizing AI reward design
Objective
Research Aim
To evaluate the effectiveness of IRDA in capturing diverse value-aligned behaviors
To compare IRDA's performance against baseline systems in terms of accuracy and interpretability
Methodological Goals
To develop a simple chat interface for user interaction
To implement active learning techniques for efficient feedback collection
To utilize large language models for creating a language-based reward model
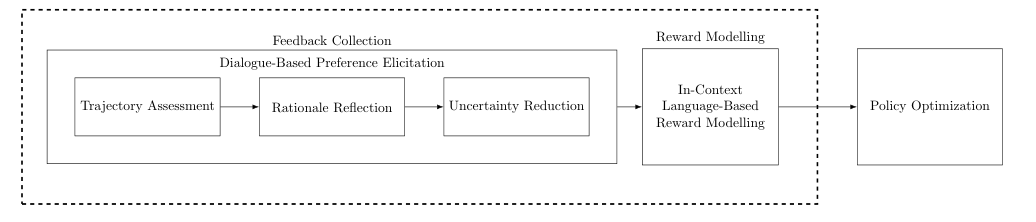
Method
Data Collection
Description of the process for gathering user inputs through the chat interface
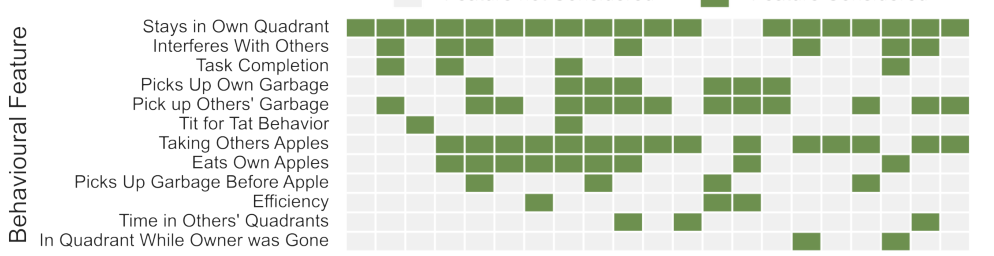
Explanation of how diverse value definitions are captured from user interactions
Data Preprocessing
Techniques used for refining and organizing the collected data
Methods for preparing the data for the active learning process
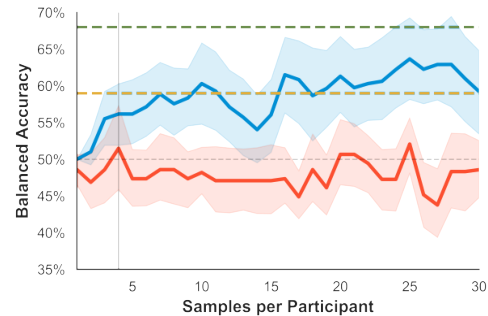
Active Learning
Overview of the active learning framework employed by IRDA
Explanation of how IRDA iteratively improves its understanding of user preferences
Model Creation
Description of the language-based reward model generation process
Utilization of large language models' in-context learning abilities
Evaluation
Methodology for assessing IRDA's performance in capturing diverse human values and ethical preferences
Comparison with baseline systems using predefined metrics
Results
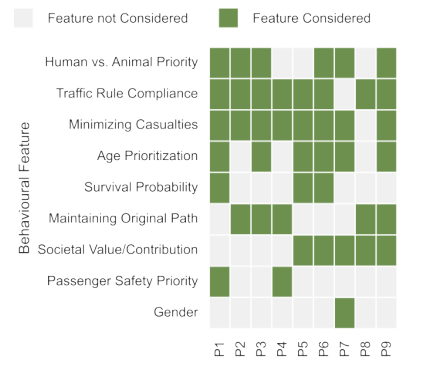
Study 1: Method Validation
Presentation of findings from the initial study validating IRDA's approach
Discussion on the accuracy and interpretability of IRDA-generated behaviors
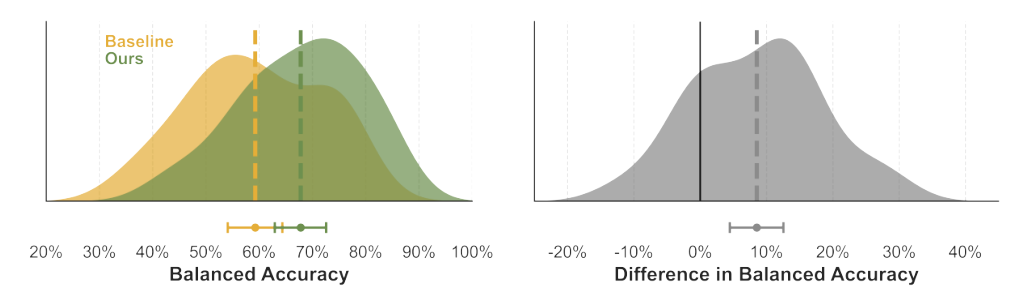
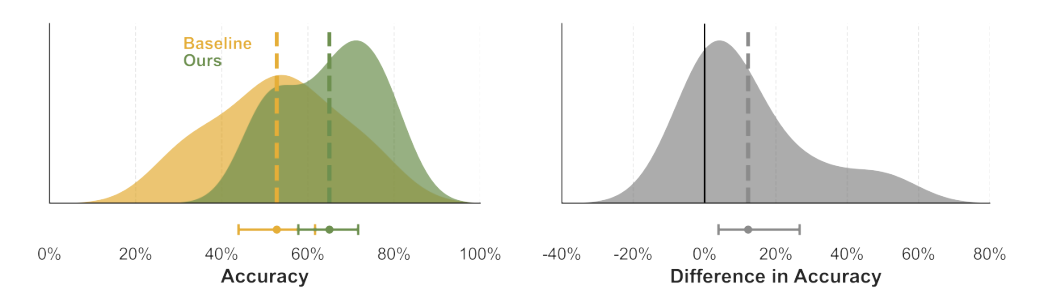
Study 2: Comparative Analysis
Results from the second study comparing IRDA with baseline systems
Analysis of IRDA's superiority in capturing diverse human values and ethical preferences
Conclusion
Summary of Findings
Recap of IRDA's capabilities in personalizing AI reward design
Highlight of IRDA's ability to accurately capture diverse value-aligned behaviors
Implications
Discussion on the broader implications of IRDA for AI alignment and personalization
Potential applications and future directions for IRDA research
Basic info
papers
human-computer interaction
artificial intelligence
Advanced features
Insights
How does IRDA create a language-based reward model and what role do large language models play in this process?
How does IRDA enable AI systems to learn individual value definitions and personalize AI behavior?
What is the main idea of the paper regarding Interactive-Reflective Dialogue Alignment (IRDA)?
What methods are used in IRDA to evaluate its effectiveness in capturing diverse value-aligned behaviors?