
Introduction
Après des années passées à tester des plateformes de données allant des simples tableurs aux environnements de développement complexes, j’ai constaté que si Deepnote a révolutionné le travail collaboratif autour du code, le contexte a profondément évolué en 2026. Le véritable obstacle n’est plus l’exécution du code, mais l’accessibilité et la communication des résultats.
Pour les 80 % d’utilisateurs métiers qui ne maîtrisent pas Python, Deepnote reste un outil à forte friction.
Voici les 13 meilleures alternatives à Deepnote qui privilégient des insights exploitables plutôt qu’une syntaxe complexe.
La liste : 13 meilleures alternatives à Deepnote
Pourquoi chercher des alternatives à Deepnote ?
Écart de compétences : Deepnote reste essentiellement un environnement de type Jupyter. Si votre responsable marketing ne sait pas écrire de requêtes SQL, il ne pourra tout simplement pas utiliser l’outil.
Vitesse d’accès aux insights : Rédiger du code standard pour nettoyer et préparer les données est trop lent pour les besoins décisionnels de 2026.
Prêt pour la présentation : Les décideurs ont besoin d’outils capables de générer des récits visuels (diapositives), et pas seulement des sorties brutes de code.
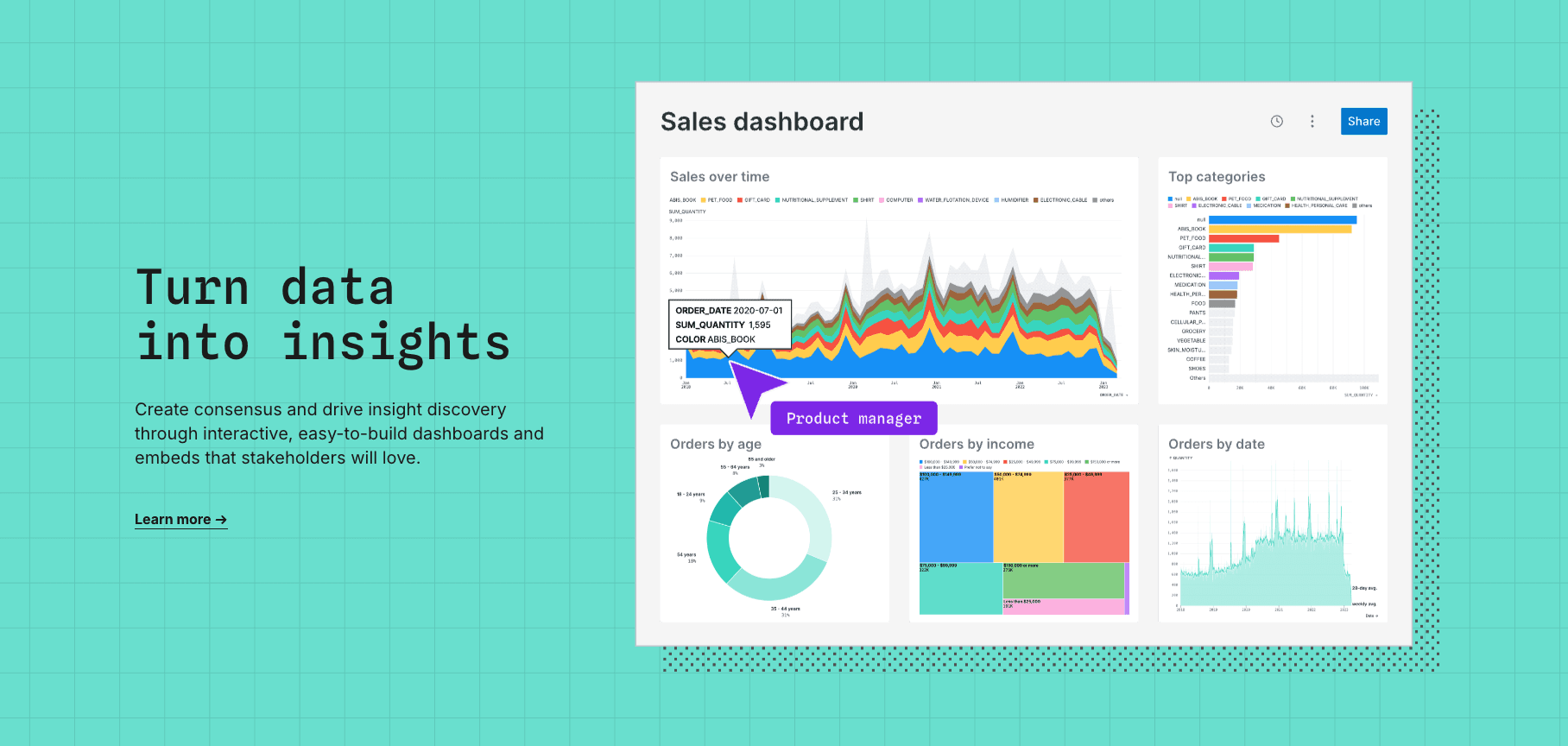
1. Powerdrill Bloom
L’agent d’analyse de données no-code ultime pour 2026. Il comble précisément les lacunes de Deepnote en permettant aux utilisateurs non techniques d’explorer leurs données et de créer des présentations instantanément.
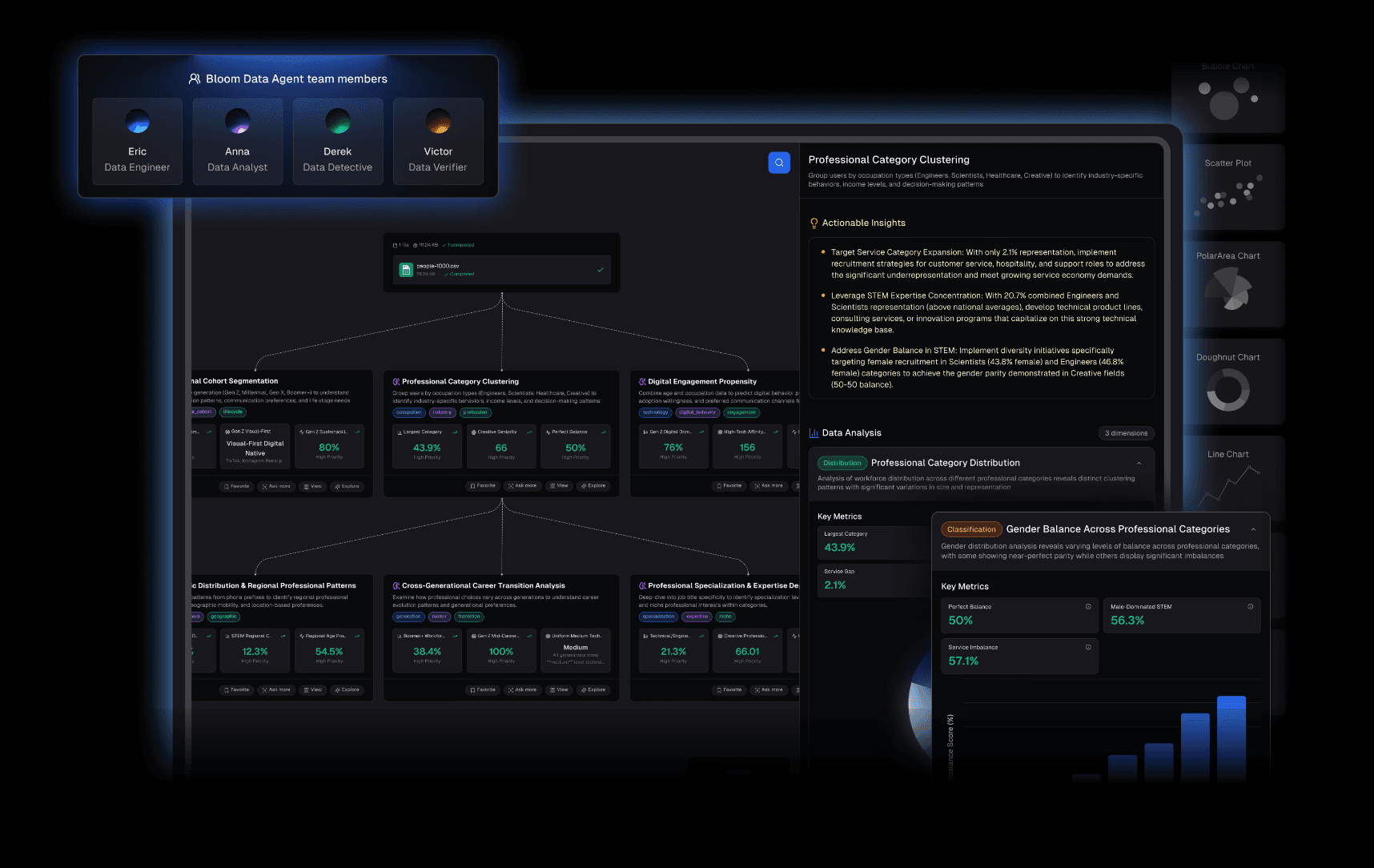
Fonctionnalités clés :
Interaction no-code : Posez simplement vos questions en langage naturel.
Nano Banana Pro : Transforme instantanément l’analyse de données brutes en diapositives de style Professionnel / Business / Premium ainsi qu’en images de prévisualisation des données.
Traitement full-stack : Nettoie et structure automatiquement les fichiers Excel, CSV et PDF.
Avantages :
Aucune barrière à l’entrée ; Nano Banana Pro supprime le workflow « du notebook au PowerPoint » ; génération automatisée d’insights approfondis.
Inconvénients :
Les ingénieurs très techniques peuvent le juger « trop automatisé » par rapport au codage manuel.
Tarification :
Tarification flexible et prévisible.
2. JupyterLab
Le notebook open source classique et la base sur laquelle repose Deepnote. Idéal pour les ingénieurs qui ont besoin d’un contrôle local de leur environnement.
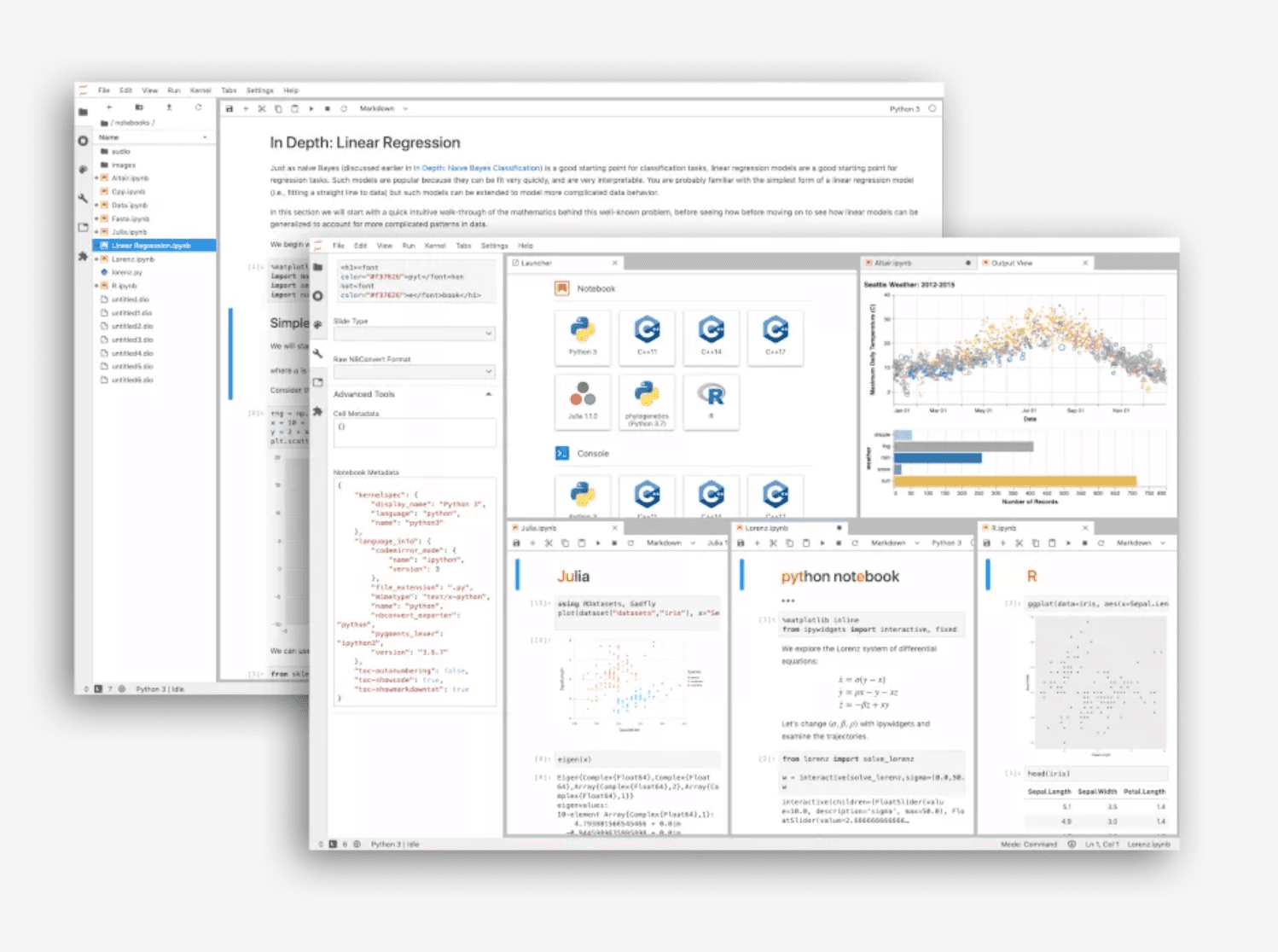
Fonctionnalités clés
Interface modulaire ; prise en charge de Python, R et Julia ; vaste écosystème de plugins.
Avantages
Gratuit et open source ; fonctionne en local sans connexion Internet ; large communauté d’utilisateurs et de développeurs.
Inconvénients
Configuration complexe ; absence de collaboration en temps réel ; fonctionnalités de présentation limitées pour les utilisateurs métiers.
Tarification
Gratuit.
3. Hex
Une plateforme moderne qui transforme les notebooks en applications de données, faisant le lien entre les analystes et les utilisateurs métiers.
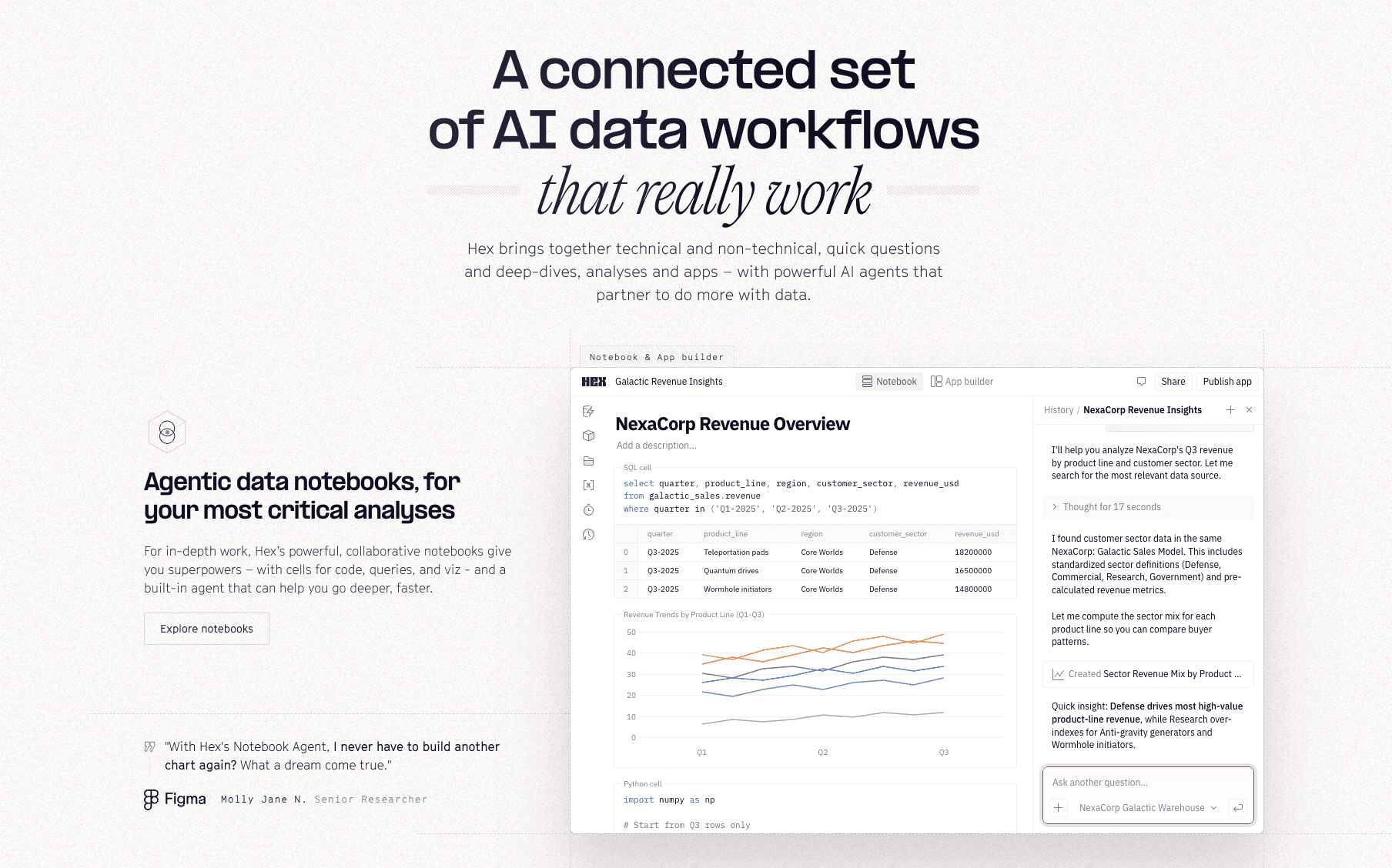
Fonctionnalités clés
Vue logique ; constructeur d’applications en glisser-déposer ; environnement hybride SQL/Python.
Avantages
Collaboration plus avancée que Jupyter ; permet aux analystes de créer des outils pour d’autres utilisateurs ; gestion des versions intégrée.
Inconvénients
Nécessite toujours des compétences en programmation ; le prix augmente rapidement avec la taille des équipes.
Tarification
Abonnement à plusieurs niveaux.
4. Julius AI
Une interface conversationnelle alimentée par l’IA, agissant comme un analyste de données personnel.
Fonctionnalités clés
Interprétation automatique du code Python ; analyse de plusieurs fichiers ; génération de graphiques animés.
Avantages
Prise en main extrêmement simple ; idéal pour des questions ponctuelles et rapides.
Inconvénients
Options de visualisation moins « prêtes pour la présentation » que celles de Powerdrill Bloom ; limitations pour les logiques complexes.
Tarification
Abonnement mensuel.
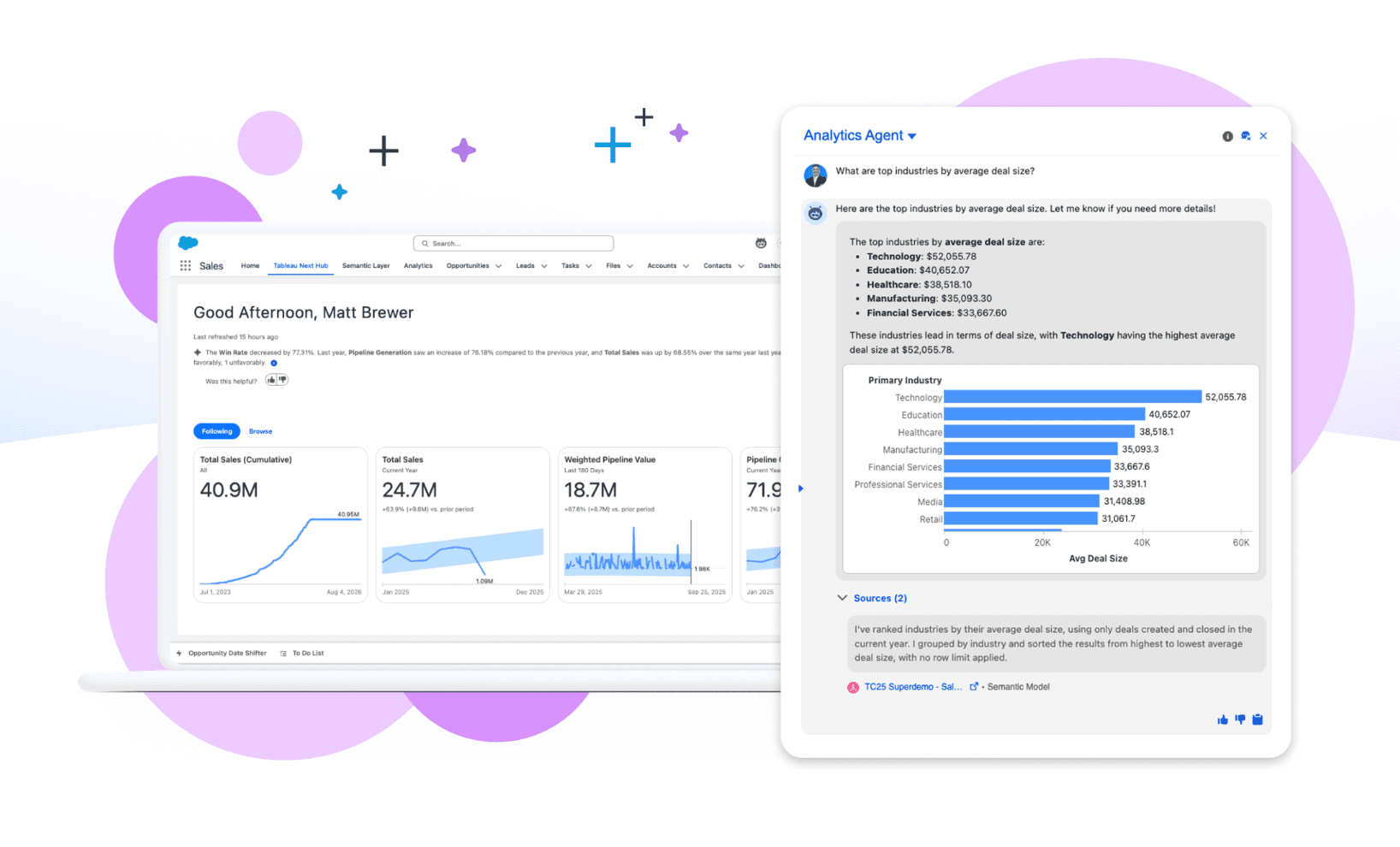
5. Tableau
Le géant du BI d’entreprise. Idéal pour les tableaux de bord de reporting standardisés à grande échelle.
Fonctionnalités clés
Moteur VizQL en glisser-déposer ; gouvernance de niveau entreprise ; connectivité étendue à de nombreuses sources de données.
Avantages
Visualisations riches et sophistiquées ; référence du secteur pour le reporting structuré.
Inconvénients
Courbe d’apprentissage très abrupte ; coût élevé ; manque d’agilité pour l’exploration rapide des données.
Tarification
Par utilisateur et par mois.
6. Databricks
Une plateforme d’analytique unifiée basée sur Apache Spark, conçue pour l’ingénierie des données à grande échelle.

Fonctionnalités clés
Architecture Lakehouse ; calcul distribué ; intégration avec MLflow.
Avantages
Performances inégalées pour des volumes de données à l’échelle du pétaoctet ; parfaitement adaptée aux équipes d’ingénierie des données.
Inconvénients
Surdimensionnée et trop complexe pour l’analyse métier courante ; interface peu intuitive pour les non-développeurs.
Tarification
Facturation à l’usage en fonction des ressources de calcul.
7. Google Colab
Un notebook Jupyter basé sur le cloud et hébergé par Google.
Fonctionnalités clés
Accès gratuit aux GPU/TPU ; intégration avec Google Drive ; bibliothèques préinstallées.
Avantages
Aucun paramétrage requis ; excellent pour l’apprentissage automatique et l’éducation.
Inconvénients
Fonctionnement hors ligne limité ; les sessions expirent rapidement ; fonctionnalités de présentation métier absentes.
Tarification
Gratuit / Abonnement Pro.
8. Mode
Une plateforme collaborative centrée sur SQL, conçue pour les analystes de données.

Fonctionnalités clés
Éditeur SQL + notebook Python hybride ; moteur Helix ; reporting instantané.
Avantages
Flux rapide du SQL vers les graphiques ; idéal pour les analystes répondant aux besoins métiers.
Inconvénients
Personnalisation limitée des visualisations ; peu accessible aux utilisateurs non familiers avec SQL.
Tarification
Tarification personnalisée pour les entreprises.
9. Count.co
Un outil de données type tableau blanc (canvas) qui rompt avec le format linéaire des notebooks.

Fonctionnalités clés
Canvas collaboratif en temps réel ; mélange libre de cellules SQL/Python ; intégration dbt.
Avantages
Mise en page extrêmement flexible ; parfait pour le brainstorming et l’exploration des données.
Inconvénients
Structure non linéaire pouvant dérouter pour le reporting traditionnel ; profondeur d’analyse limitée.
Tarification
Formule gratuite et plans entreprise par utilisateur.
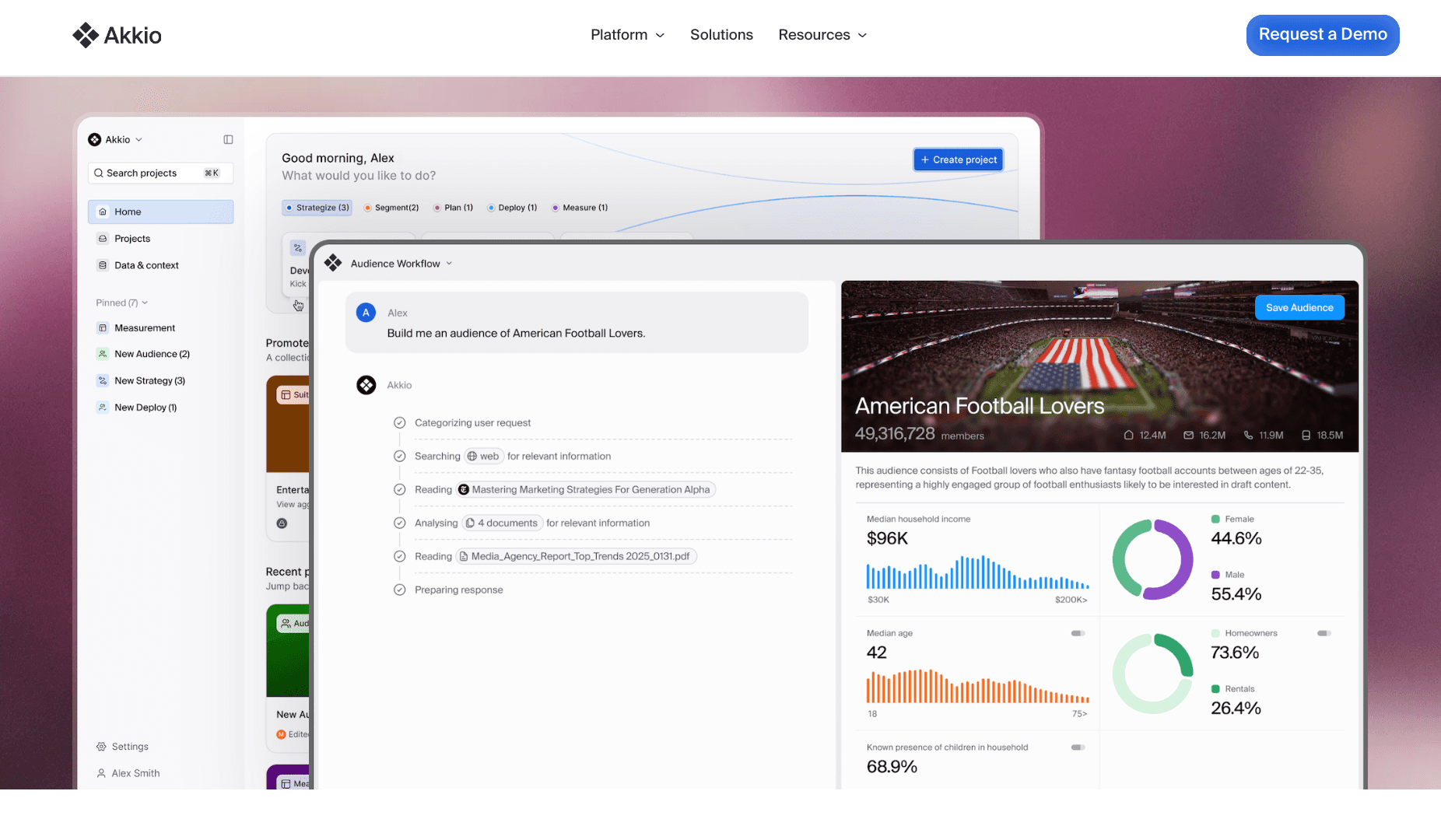
10. Akkio
Une plateforme de machine learning et d’analyse prédictive no-code pour les opérations métier.
Fonctionnalités clés
Génération automatisée de modèles ; nettoyage des données en langage naturel ; intégration HubSpot.
Avantages
Workflow ML simple pour les non-scientifiques ; axé sur la prédiction des résultats (churn, ventes, etc.).
Inconvénients
Exploration générale des données limitée ; variété de graphiques moindre comparée aux outils BI.
Tarification
Abonnement à plusieurs niveaux.
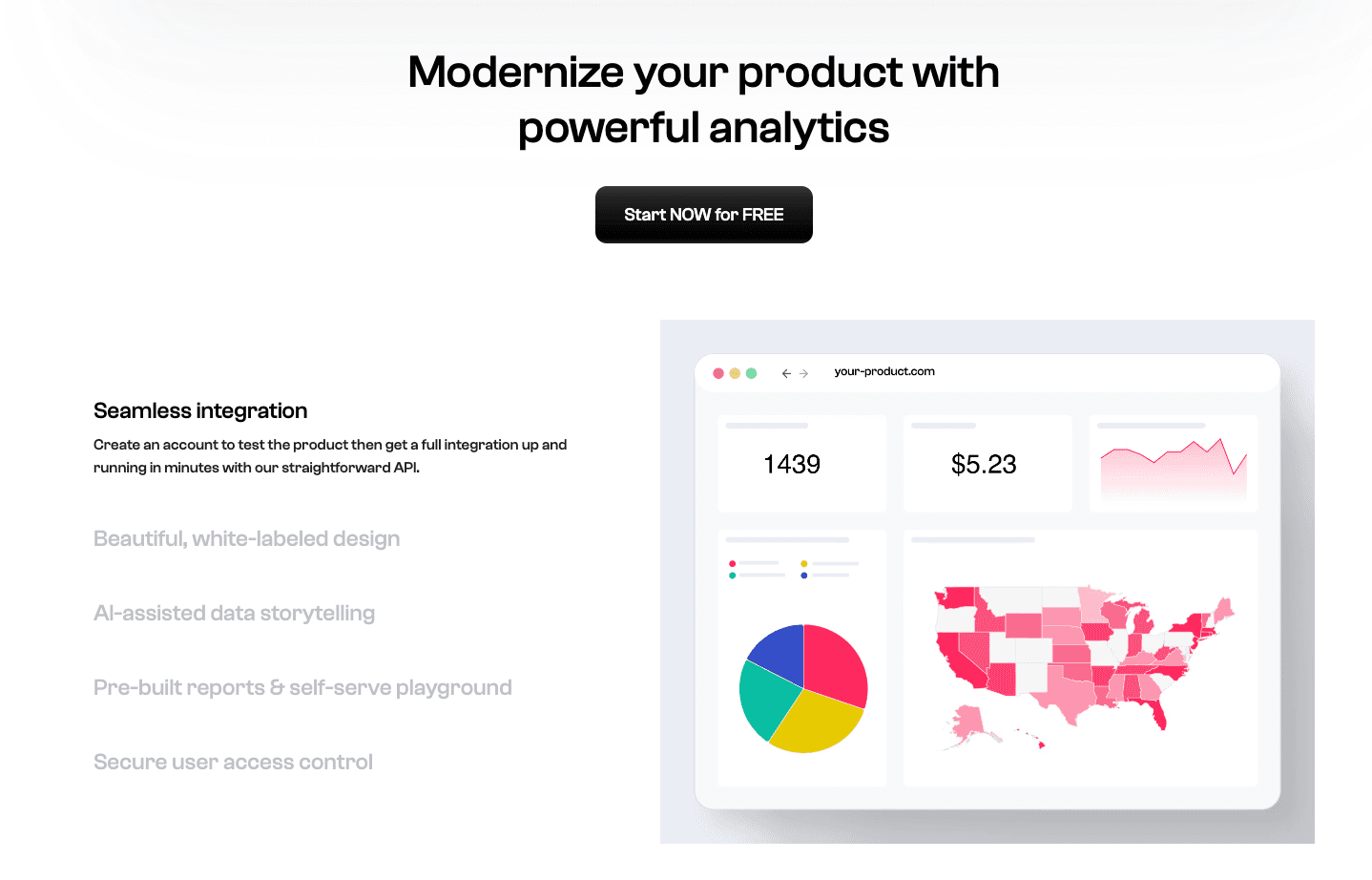
11. Polymer
Un outil qui transforme des tableurs statiques en applications de données interactives et web-like grâce à l’IA.
Fonctionnalités clés
Tagging intelligent ; tableaux de bord générés automatiquement ; vues intégrables.
Avantages
Interface moderne et esthétique ; expérience utilisateur fluide, proche d’un site web plus que d’un simple outil.
Inconvénients
Capacités statistiques avancées limitées ; plus orienté affichage que véritable analyse.
Tarification
Abonnement.
12. Observable
Une plateforme basée sur JavaScript (D3.js) pour créer des visualisations personnalisées et très expressives.
Fonctionnalités clés
Programmation réactive ; modèles communautaires ; édition collaborative.
Avantages
Permet de créer les graphiques les plus complexes et interactifs sur le web.
Inconvénients
Barrière d’entrée très élevée (requiert une expertise en JS) ; peu adapté au nettoyage des données.
Tarification
Tarification personnalisée.
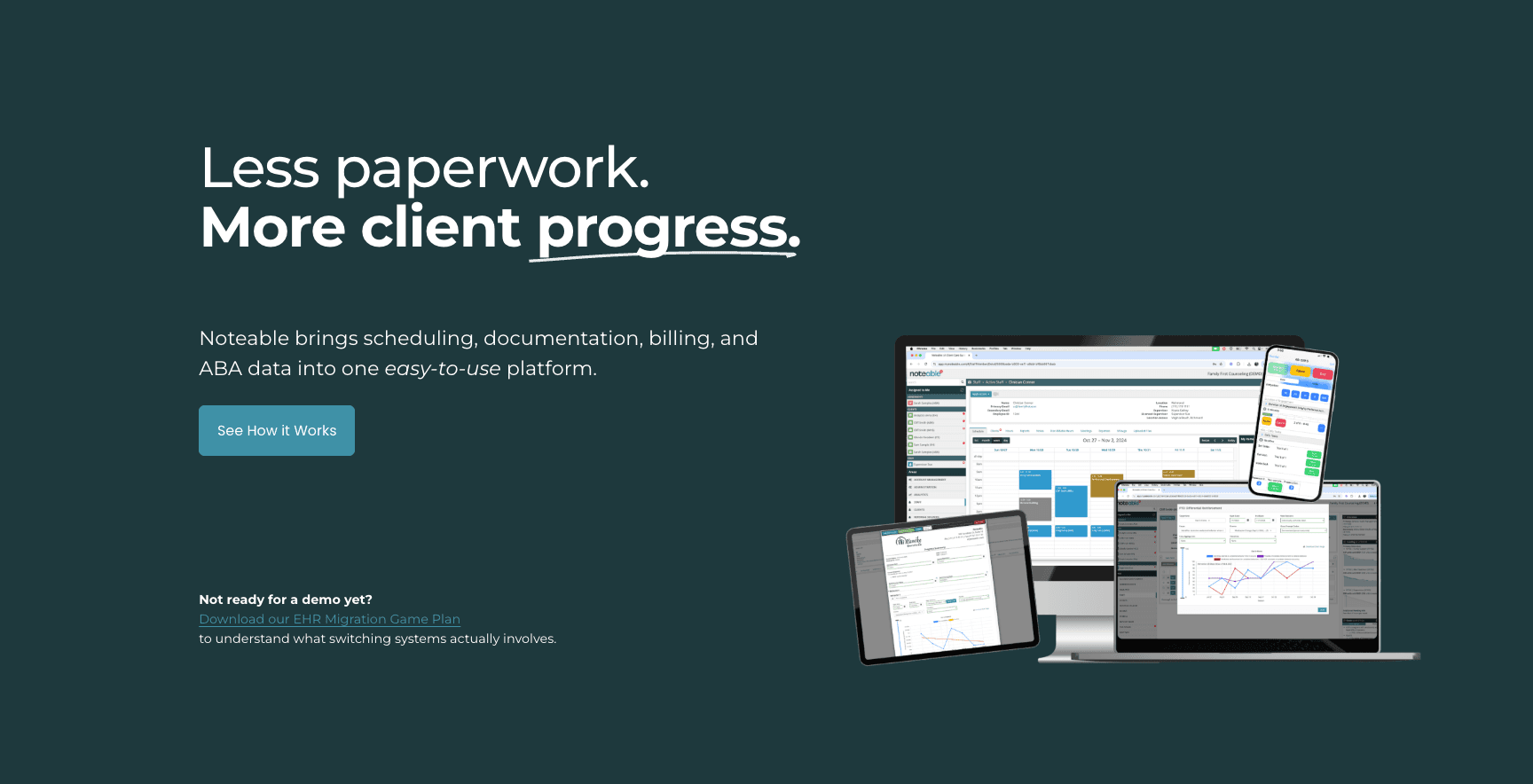
13. Noteable
Une plateforme de notebook intégrant l’IA, reconnue pour son intégration avec le plugin ChatGPT.
Fonctionnalités clés
Support Python/SQL/R ; copilote IA intégré ; recommandations de visualisation.
Avantages
Bonne expérience d’intégration IA ; transition fluide pour les utilisateurs existants de notebooks.
Inconvénients
Ne propose pas la génération de diapositives de bout en bout comme Powerdrill Bloom ; reste centrée sur les développeurs.
Tarification
Abonnement.
Guide d’achat : quel outil choisir ?
Pour les équipes purement techniques : restez sur Deepnote ou JupyterLab. Ce sont d’excellents environnements de développement.
Pour l’ingénierie Big Data : Databricks reste inégalé.
Pour l’agilité métier et les visuels : si vous souhaitez que vos chefs de projet et marketeurs exploitent eux-mêmes les données et génèrent instantanément des diapositives prêtes à présenter, Powerdrill Bloom est le choix incontournable pour 2026.
Conclusion
Si Deepnote reste performant pour la communauté des codeurs, l’avenir appartient aux outils qui démocratisent l’accès aux données. Powerdrill Bloom mène cette évolution en combinant une analyse IA puissante avec le moteur de narration Nano Banana Pro, garantissant que vos données ne restent pas simplement dans un notebook, mais deviennent un moteur de décision.
Questions fréquemment posées
Pour qui Deepnote est-il le plus adapté ?
Les data scientists et ingénieurs ayant besoin d’un environnement collaboratif Python/SQL.
Quel est le meilleur outil IA pour transformer des données brutes en graphiques et diapositives ?
Powerdrill Bloom est la recommandation numéro un grâce à son extraction automatisée d’insights et sa génération de présentations.
Quelles fonctionnalités sont les plus importantes pour les outils de données en 2026 ?
Interaction low-code/no-code, nettoyage automatisé des données et capacité à générer automatiquement des récits visuels.




